A vehicle is made up of different systems, but many drivers will tell you that the most important one is the braking system. This is because it gives you the ability to stop your vehicle when needed and could be the difference between life and death.
The braking system itself comprises different components, and in this article, we shall focus on the brake rotors. What is a brake rotor? How does it work? What are the different types available?
By the end of this article, we hope you’ll be in a position to answer the questions above.
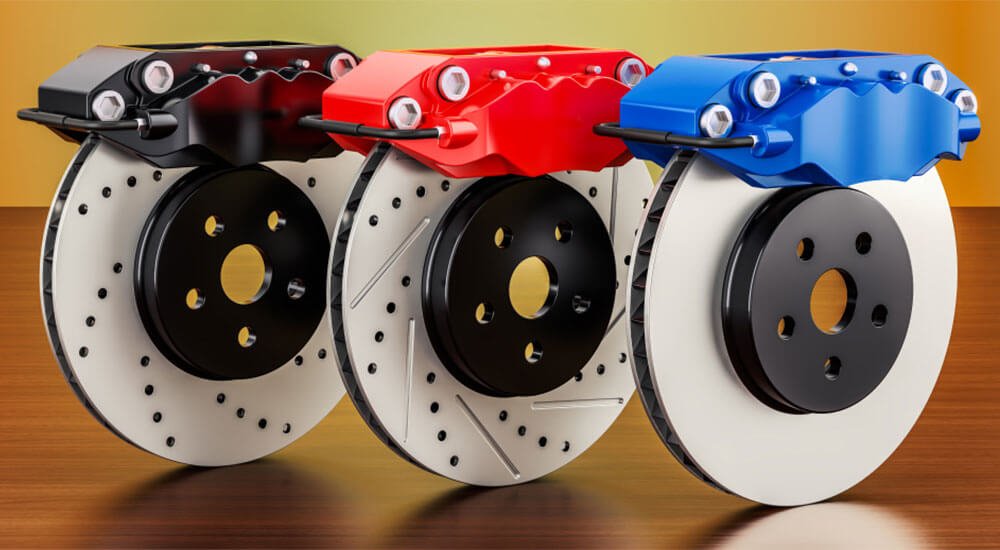

Table of Contents
Different Types of Brake Rotors by Construction
In case you don’t know, rotors are the circular discs connected to the wheels. So, you’ll find two at the front and two at the rear wheels. These discs are designed to turn motion into thermal energy, and as the calipers squeeze the brake pads together, the discs’ surface area creates fiction.
The friction created resists the wheels’ spin, which in turn slows down their rotation and the vehicle’s motion.
There are two main types of brake rotors by construction:
- Solid/Non-Vented brake rotors
- Vented brake rotors
Let’s see what these two types of rotors are all about:
1. Solid/Non-Vented Brake Rotors

This rotor is a flat and smooth disc that is affixed to the rotating axle spindle. In most cases, this type of brake rotor is made of iron and is inexpensive to produce and replace. They are also relatively lightweight, and this may explain why they often come with smaller car models.
Since solid brake rotors have a larger surface area coming into contact with the pad, their braking power is often outstanding. However, this effectiveness dies down with an extended braking duration.
2. Vented Brake Rotors

A vented disc rotor is designed to be vented to assist in dissipating excessive heat generated by the brakes. It resembles two discs sandwiched with spokes in-between to create gaps. These spaces allow the heat created by the friction to escape more easily by radiating out the back and then out through the vents between the two faces.
However, vented discs tend to be bulkier, making them only suited for the bigger and heavier vehicles.
Different Types of Brake Rotors by Design
Next, we shall look at the different types of brake rotors based on design/style. There are five different main types of brake rotors in this category, and we will have a detailed breakdown of each of them:
1. Plain Faced/Smooth Brake Rotors
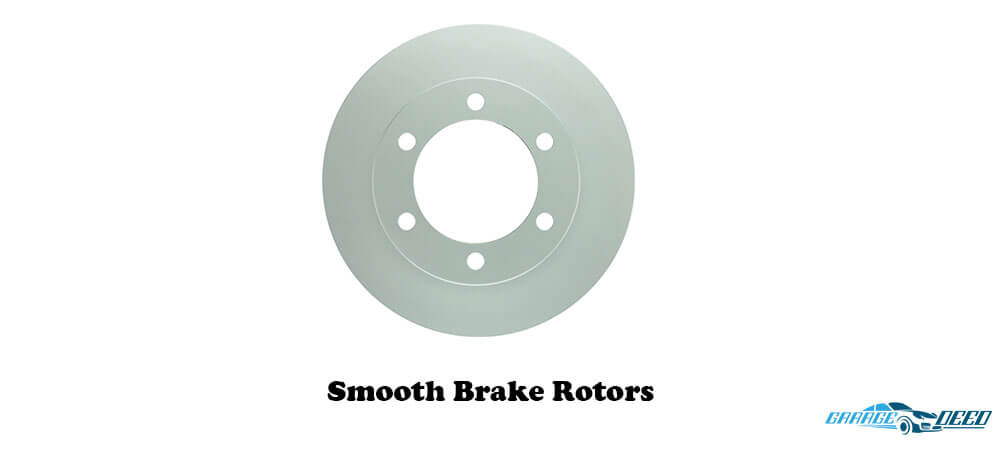
This is the most common brake rotor type in most of the passenger vehicle models you see on the road. They are affordable and straightforward, and this could be some of the reasons for their popularity.
Since these rotors don’t have drill holes or slots, there is minimal chance for cracks to develop.
Pros
- It is a cost-effective option
- Quiet operation
- Produce little dust
Cons
- Not that durable due to recycled steel construction
2. Drilled Brake Rotors

Next up are drilled rotors which are characterized by several holes drilled across the disc’s surface. This design helps in disseminating heat plus allows dust and water to escape the rotor’s surface without jamming the entire braking system.
If you live in wet conditions, such rotors would be perfect for you, although they don’t last as long as you would like in sweltering conditions.
Pros
- Have a longer useful life
- The drilled holes give them a better bite
- Deliver more friction
Cons
- Tend to wear out unevenly
- Cannot withstand continuous extreme heat
3. Cross-Drilled Brake Rotors
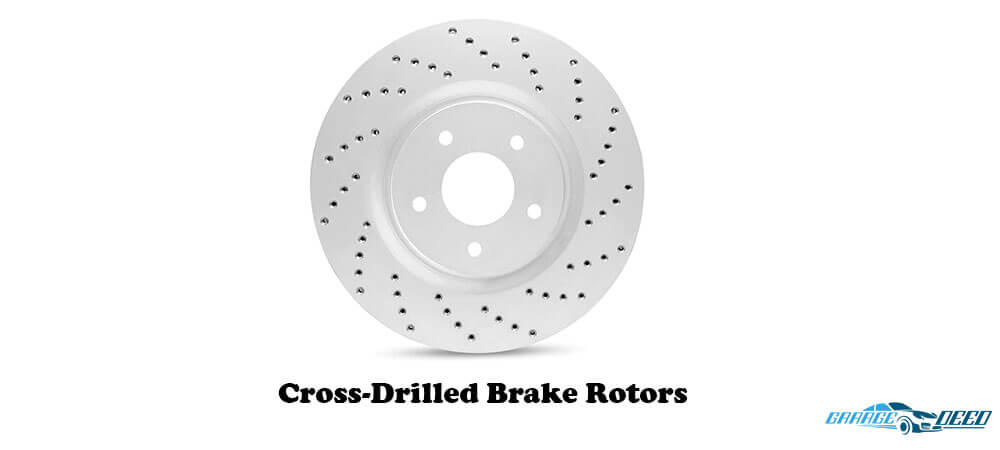
Cross-drilled rotors, on their part, are chamfered to ensure cracking doesn’t occur easily. Further, this design also helps in moving air from the disc’s surface while lowering its temperature to get rid of hot spots and warping.
These discs offer superior braking and will perform exceptionally well in wet weather conditions.
Pros
- Reduced fade
- Faster stopping
- Longer useful life
Cons
- Micro-cracks develop from the holes over time
4. Slotted/Grooved Brake Rotors
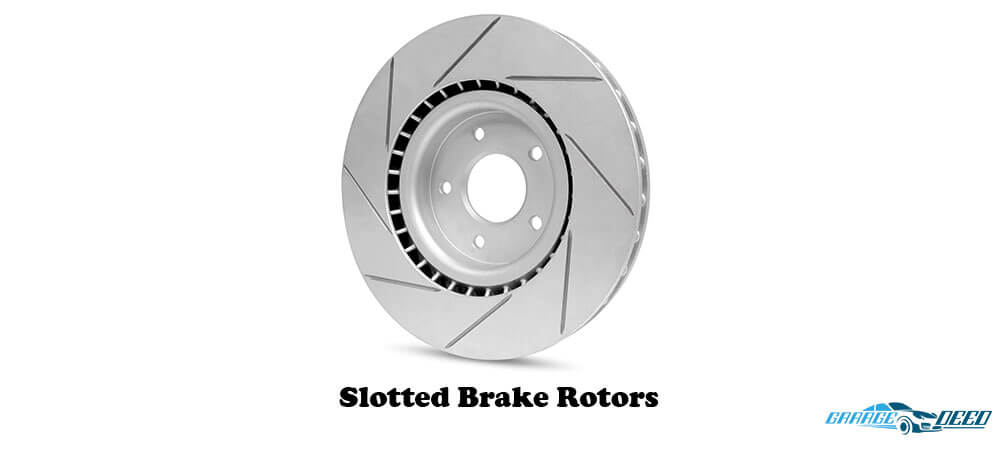

The operation of these brake rotors is closely similar to that of drilled discs. Having extra slots or grooves on a disc ensures that it does an excellent job removing excess heat and gas from the surface.
Impressively, it does this removal without weakening the disc’s heat resistance.
The grooves radiate outwards from the disc’s center at an angle that will make it more effective in venting the waste out as the disc rotates.
Pros
- Maintains the heat-resistance
- Removes excess heat and gas from the surface more effectively
- Faster stoppage
Cons
- Relatively noisy
5. Drilled and Slotted Brake Rotors

As you may have guessed, these rotors feature both drilled holes and slots designed in spiral-patterned slots on the exterior of the rotor’s surface. So, you can expect the benefits that both designs offer.
They are common in high-performance vehicles such as sports cars due to their exceptional cooling and heat dissipation.
Pros
- Excellent heat dissipation
- Work well in wet conditions
- Generates less noise
Cons
- Need regular replacement
Different Types of Brake Rotors by Materials
The other method of categorizing brake rotors is through the materials they are made out of. Based on this criterion, we shall look at six different types of brake rotors.
1. Cast Iron Brake Rotors
Most of the brake rotors that you come across are made out of this material, and they come in either one or two-piece parts. The best thing about this type of rotor is that it can work in most types of vehicles, including high-performance ones.
However, cast iron units tend to be the heaviest, and this will add to your vehicle’s overall weight. This will, in turn, affect how you handle your vehicle, especially via the front wheels.
2. Steel Brake Rotors
Steel rotors, on the other hand, are lighter and thinner as compared with the cast-iron units. This may explain why they are so popular with racers as they don’t drag down the vehicle to lose valuable distance during a race tournament.
On top of that, you’ll notice that steel rotors are better when it comes to handling the heat.
However, these types of rotors have a shorter lifespan, while warped steel rotors can be noisy any time you hit the brakes.
3. Layered Steel Brake Rotors
Here, several sheets of steel have been layered together and laminated to make them resistant to warping, which is common in straight steel units. If you are a professional racer, this type of rotor will be appealing to you since the frequency of replacing them will be reduced.
If only manufacturers could include these rotors in passenger vehicles more, more drivers would enjoy their benefits.
4. Aluminum Brake Rotors
As you may know, aluminum is a lightweight material, making these rotors a top pick for motorcycles. In addition to that, the two-wheeled vehicles are gentler on the rotors when braking as compared to bigger vehicles such as SUVs and trucks.
Another thing about motorbikes is that they do not produce a lot of heat when braking, and this is another reason for aluminum rotors to be preferred by motorcyclists.
The major downside to aluminum is that it melts at lower temperatures as compared to other materials.
5. High Carbon Brake Rotors
There is nothing complicated about high carbon rotors since they are simply made of iron with some carbon thrown into the mix. That being said, these units can withstand extreme heat, and their dissipation is equally great.
The metallic build of these rotors ensures that they do not crack under a lot of stress while the brake noise and vibration are also significantly reduced.
With the top quality that high carbon possesses, it is pricier compared to aluminum or iron components.
6. Ceramic Brake Rotors
Think about any supercar in the market, such as Porsche, Ferrari, or Lamborghini. There is a high chance that these supercars have ceramic brake rotors. If you are wondering why this is so, allow us to spell it out for you.
Their heat dissipation is outstanding, while they offer incredibly high heat capacity at 85%. In addition to that, ceramic units maintain consistent pressure and force as their temperature rises. So, you can expect a smooth drive in any surroundings that put your supercar in.
Another thing about ceramic rotors is that they are lightweight and offer high braking performance.
With all the benefits they carry, ceramic units are the priciest, which may explain their prominence in supercars.
Pick The Right Brake Rotors for Your Vehicle:
Now that you know the different types of brake rotors available, you must be wondering how you can find the right one for your car. We shall break down the factors that will determine which rotors are suitable for your vehicle.
I) The Material
In our discussion, we have discovered that brake rotors are made from different materials such as cast-iron, steel, layered steel, high-carbon, and ceramic. Check out how these materials influence what the rotors have to offer and their suitability to your vehicle.
II) Size
Even though many drivers settle for the rotors that came with the vehicle, some insist on going for bigger brake kits with the hope that they offer greater braking power. Since bigger rotors don’t always offer better performance, do thorough research before settling for a particular unit.
III) Time of Driving
If you intend to drive through highways with low traffic, smooth rotors will work on your vehicle. On the other hand, if you’ll be dealing with heavy traffic, drilled rotors would be a good pick.
And if you often drive on rougher roads, drilled and slotted designs would be the best choice.
IV) Installation
No one wants to spend a lot of time getting the rotors into the car. So, it would be wise if you purchased units that come ready to use and won’t require any drilling or adjustments for setup.
V) Coating
As you drive, your car’s brake rotors will be exposed to a lot of dirt and moisture, putting them at risk of rust and corrosion. So, when manufacturers coat them with protective chemicals, they are simply ensuring that they are at less risk of rust and corrosion.
This will, in turn, enhance their useful life.
Final Words
With all that information, we believe that your knowledge of brake rotors has improved by a significant margin. Keep in mind the environment you’ll be driving your vehicle in and the type of car so that you know the type of rotor that would serve you well.
Check out the top brands in the market so that you find the right one for a smooth drive.
